Intraoral scanners are advanced dental technology devices used to create digital impressions of a patient’s teeth and oral structures. These scanners replace the traditional method of using physical impression materials like dental putty and alginate to capture the shape of a patient’s teeth and gums.
How Intraoral Scanners Work:
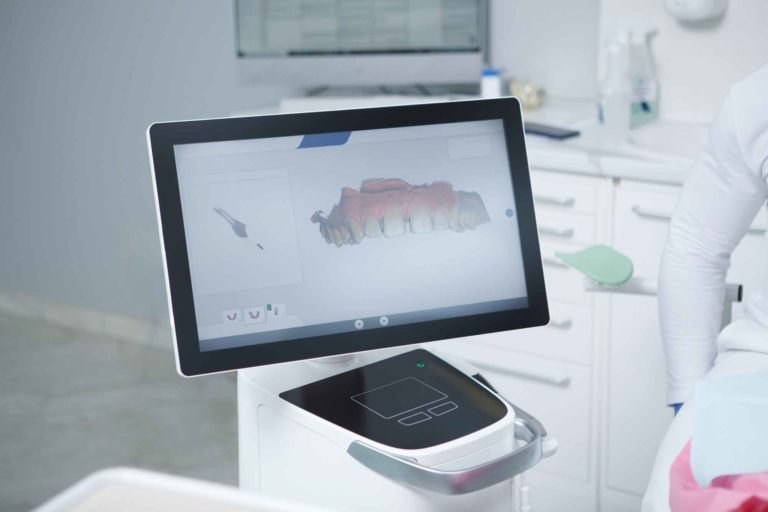
Intraoral scanners use optical scanning technology to create a 3D digital model of a patient’s mouth. The scanner is a handheld device that the dentist or dental assistant places inside the patient’s mouth. As the scanner moves around, it captures multiple images of the teeth and oral tissues, which are then stitched together by software to create a comprehensive digital impression.
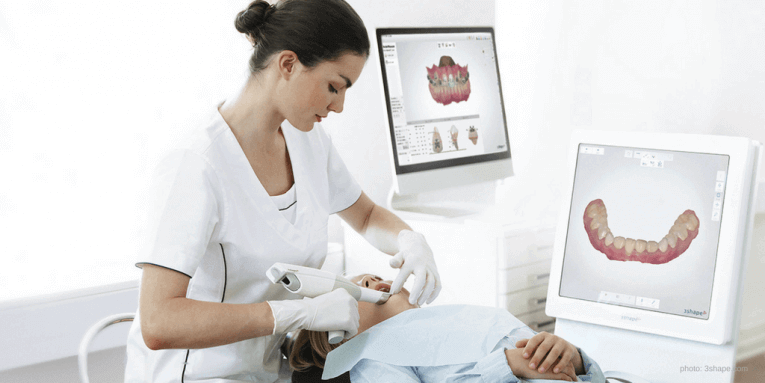
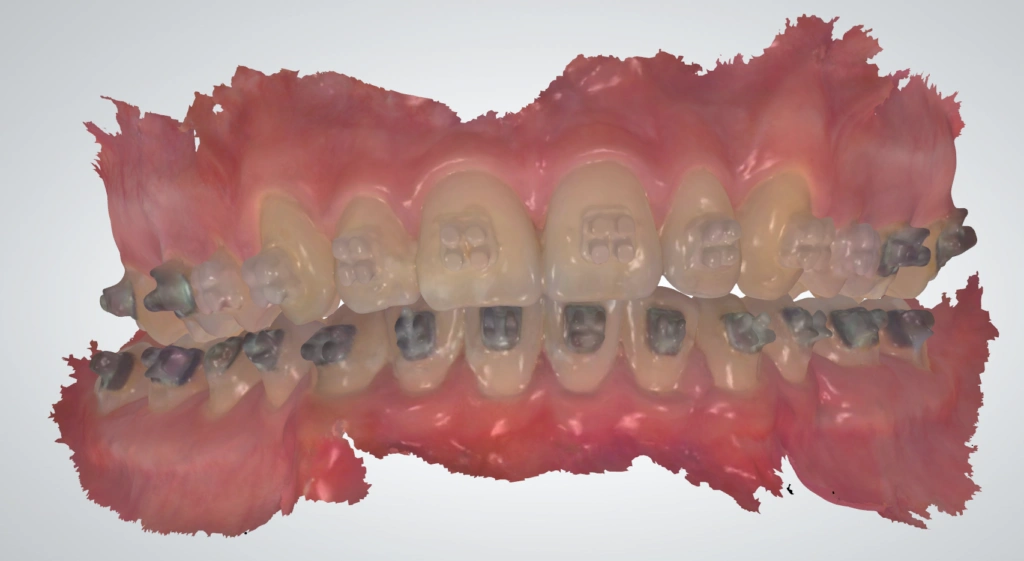
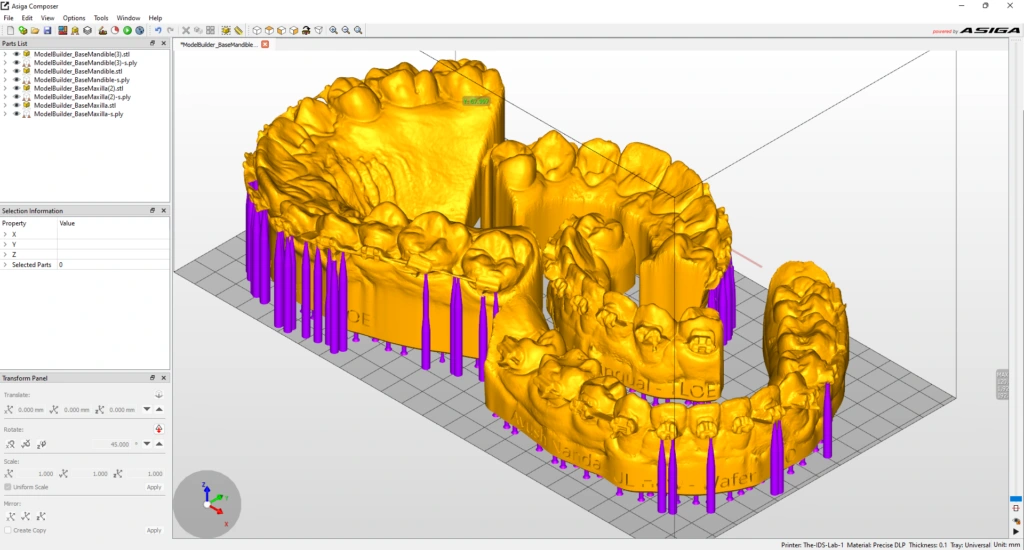
Benefits of Intraoral Scanners for Dental Laboratories:
Accuracy: Intraoral scanners offer high precision and accuracy in capturing the details of a patient’s dental anatomy. This reduces the chances of inaccuracies that might occur with traditional impressions and leads to better-fitting restorations and appliances.
Time Efficiency: Digital impressions with intraoral scanners are faster to capture than traditional impressions, which can be messy and time-consuming. The digital process eliminates the need for physical materials and shipping, streamlining the workflow for both the dental practice and the dental laboratory.
Improved Communication: The digital nature of intraoral scans allows for easy and quick transfer of information between the dental practice and the dental laboratory. Dentists can send the digital impressions electronically to the lab, reducing the risk of errors or miscommunication that can occur when using physical impressions.
Reduced Remakes: The accuracy of intraoral scanners helps minimize the need for remakes due to impression inaccuracies. This saves time and resources for both the dental practice and the dental laboratory.
Enhanced Productivity: With intraoral scanners, dental laboratories can handle a higher volume of cases efficiently. The digital workflow enables technicians to work on multiple cases simultaneously, leading to increased productivity and faster turnaround times.
Digital Storage: Digital impressions are easy to store securely in a digital format. This eliminates the need for physical storage space for bulky impression moulds, making it easier for dental laboratories to manage patient records and archives.
CAD/CAM Integration: Intraoral scanners can be seamlessly integrated with computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems. This integration allows dental laboratories to design and manufacture restorations (e.g., crowns, bridges, implants) digitally, further enhancing precision and efficiency.
In summary, intraoral scanners benefit dental laboratories by providing more accurate, time-efficient, and streamlined workflows. The digital nature of these scanners improves communication between dental practices and laboratories, reducing the likelihood of errors and remakes while increasing overall productivity. With the continued advancement of digital dentistry, intraoral scanners have become an essential tool for modern dental laboratories seeking to deliver high-quality dental restorations to patients.